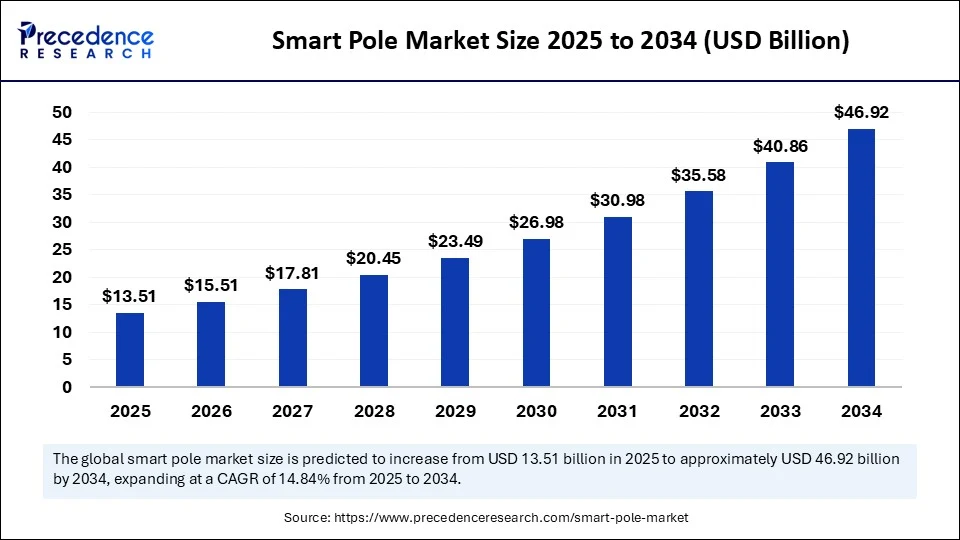
The global smart pole market size is estimated to surpass around USD 46.92 billion by 2034 increasing from USD 11.76 billion in 2024, with a CAGR of 14.84%.
Smart Pole Market Key Takeaways
- In terms of revenue, the global smart pole market was valued at USD 11.76 billion in 2024.
- It is projected to reach USD 46.92 billion by 2034.
- The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 14.84% from 2025 to 2034.
- North America dominated the largest smart pole market share of 34% in 2024.
- Asia Pacific is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 20.8% during the foreseeable period.
- By offering, the hardware segment accounted for the biggest market share in 2024.
- By offering, the software segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 22% during the foreseeable period.
- By installation type, the retrofit segment contributed for the highest market share in 2024.
- By installation type, the new installation segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the foreseeable period.
- By application, the highways and roadways segment captured the remarkable market share in 2024.
- By application, the public places segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 20% during the foreseeable period.
- By connectivity tech, the cellular (4G/5G/NBIoT) segment accounted for the largest market share in 2024 and expected to sustain its position during the foreseeable period.
- By material, the metallic segment generated the major market share of share in 2024.
- By material, the composite segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 21% during the foreseeable period of 2025-2034.
How is AI Transforming the Smart Pole Market?
AI-powered smart poles offer transformative potential in urban planning by enabling features like predictive traffic analysis, dynamic lighting control, and advanced surveillance capabilities. By analyzing historical patterns and real-time data, AI systems can forecast traffic congestion and suggest alternate routing strategies. These smart poles also regulate LED brightness based on activity levels, improving energy efficiency and lowering light pollution. Additionally, real-time monitoring and AI-based threat detection enhance public safety infrastructure.
Market Overview
The smart pole market has matured from niche smart city pilots into a thriving infrastructure category, expected to grow robustly over the coming decade. The market encompasses hardware providers, integrators, telecom operators, software platforms, smart utilities, security services and analytics businesses. Street‑lighting systems are evolving into multifunctional digital infrastructure nodes. Adoption is especially strong across municipal (smart city), corporate campus, transportation (airports, ports, highways) and educational environments.
Capital deployment varies widely—from small US and European pilot zones to large scale deployments across Asian mega‑cities and Gulf states. Market size is dominated by a combination of equipment sales and value‑added services (software, analytics, maintenance). With global emphasis on sustainability, connectivity, and smart surveillance, the smart pole market is firmly embedded in both urban planning and telecom infrastructure strategies.
Market Drivers
-
Economic efficiency and lifecycle savings: Retrofit smart lighting and IoT capabilities reduce energy and maintenance costs, leading to significant savings over time. City budgets are increasingly allocated toward future cost reduction rather than only capex.
-
Regulatory and policy incentives: Government initiatives promoting smart infrastructure, energy efficiency, reduced light pollution, and public safety have provided significant funding or subsidized models. Many grant programs now explicitly include smart pole technologies as eligible infrastructure.
-
Telecom densification mandates: Telecom carriers are under pressure to meet 5G rollout targets, especially in dense urban areas. Municipal agreements to host small cells on smart poles help carriers bypass expensive tower builds and zoning delays.
-
Public safety and law enforcement requirements: Rising concerns over crime, traffic accidents, and emergency response have heightened interest in deploying surveillance, public announcement systems, and real‑time monitoring—capabilities inherent to advanced smart poles.
-
Smart LED lighting adoption: Municipal investment in LED lighting conversion provides a natural gateway for upgrading to smart poles. As cities replace traditional sodium or halide street lights to LEDs, there is a strong propensity to integrate intelligence in tandem.
Market Opportunities
-
Managed services and SaaS models: Market players are shifting toward recurring‑revenue models, offering managed lighting-as‑a‑service, connectivity as‑a‑service, analytics dashboards, and SLA‑backed operations. This trend broadens market appeal, especially to municipalities without in‑house technical capabilities.
-
Greenfield smart city zones: Developing smart city zones in new towns or urban extensions—particularly in Asia, the Middle East, and Latin America—provide opportunities to implement smart pole networks as core infrastructure, not retrofits.
-
Cross‑industry collaborations: Smart pole schemes are expanding into collaborations with companies in transportation, logistics, advertising, EV charging, retail, and utilities—creating shared value networks and bundled service offerings.
-
Data monetization and analytics platforms: Data generated by smart poles—traffic density, air pollution, pedestrian flow—can feed city situational awareness, commercial analytics, and targeted digital advertising, unlocking new monetization possibilities.
-
Customization and modularization of offerings: Suppliers that provide modular, plug‑and‑play modules (e.g. for environmental sensors, cameras, signage, EV fast‑charging) make it easier for cities to adopt based on phased budgeting and evolving needs.
Market Challenges
-
Fragmented stakeholder landscape: Smart pole projects often involve municipalities, telecom providers, lighting companies, vendors, analytics firms and maintenance contractors—and aligning incentives and responsibilities among multiple stakeholders proves complex.
-
Lack of standards and interoperability: Absence of universal technical and communication protocol standards hinder seamless integration of components from different vendors. Proprietary systems may lock cities into vendor ecosystems.
-
Data security and cybersecurity risks: Smart poles with networked sensors and compute modules are potential cyber‑attack vectors. Ensuring secure firmware, encrypted communications, and compliant data governance increases deployment complexity and operational overhead.
-
Long implementation timelines and pilot‑itis: Many cities linger in pilot and proof‑of‑concept phases for prolonged periods, slowing commercial scale‑up. Some fall into “pilot‑itis,” where small rollouts don’t transition into full deployments due to budget cycles, changing leadership or lack of clear ROI.
-
Maintenance burdens: Urban installations are exposed to weather, vandalism, wear‑and‑tear. Mixed technology stacks mean varied maintenance tasks—lighting, sensor calibration, charging connectors, signage screens—all require routine servicing and technical expertise.
Recent Developments
-
Investor interest and M&A activity: In recent months, venture capital and private equity firms have backed startups specializing in smart pole modular hardware, edge computing analytics, and integrated lighting/connectivity platforms. Several acquisitions and partnerships signal consolidation momentum.
-
Standardization efforts underway: Industry consortia and smart‑city alliances have initiated work on interoperability standards for smart pole telemetry, sensor integration and 5G small‑cell compatibility—though formal standards bodies have yet to finalize specifications.
-
Advanced edge and analytics features: New product lines incorporate onboard GPU/TPU edge AI modules enabling video analytics, pedestrian counting, anomaly detection, real‑time traffic signal coordination and localized announcements.
-
Sustainability embedded in hardware: Smart pole designs increasingly feature solar or wind power subsystems, recyclable pole materials, carbon tracking across lifecycle, and night‑mode dimming to reduce light pollution.
-
Global expansions: Companies previously focused on Europe and North America have launched deployments in India, Brazil, Middle East cities—leveraging growing demand from rapidly urbanizing regions. Retrofit kits adapted to local pole architectures have eased localization.
-
Pilot to scale transitions: Many cities that conducted pilot deployments—typically 50–200 units—are now scaling to 500+ smart poles across multiple districts, integrated with centralized management dashboards tied into broader city IoT hubs or command‑control centers.
Get Sample@ https://www.precedenceresearch.com/sample/6419
Smart Pole Market Companies
- Acuity Brands Lighting
- American Tower Corporation
- Bivocom
- Cree Inc.
- Efftronics Systems
- ELKO EP
- GE (General Electric)
- HUB Group
- iRam Technologies
- Kesslec
- Lumca Inc.
- Mobile Pro Systems
- Norsk Hydro ASA
- Signify Holding
- Shanghai Sansi Electronic Engineering
- Siemens AG
- Sunna Design
- Telensa Limited
- Wipro Lighting
- Zumtobel Group
Segments Covered in the Report
By Offerings
- Hardware (poles, luminaires, sensor modules, communication devices, controllers)
- Software (management, analytics platforms)
- Services (installation, maintenance)
By Installation Type
- New Installation
- Retrofit Installation
By Application
- Highways & Roadways
- Public Places (parks, plazas)
- Railways & Harbors
By Connectivity Technology
- Cellular (4G/5G/NBIoT)
- Wi-Fi, Zigbee, Bluetooth, Fiber, PLC
By Material
- Metallic (steel, aluminum)
- Composite (emerging lightweight materials)
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
Also Read: https://www.precedenceresearch.com/